The Future of Surgery: How AI Robots Are Changing the Operating Room
Published: 25 Apr 2025
Can a robot really help a surgeon in performing an operation without any damage? It sounds strange but it’s the reality. AI robots in surgery are changing how doctors work in the operating room. Doctors guide the movements of AI robots which reduce human errors and help in patients’ recovery. Curious how that works? Let’s explore it.
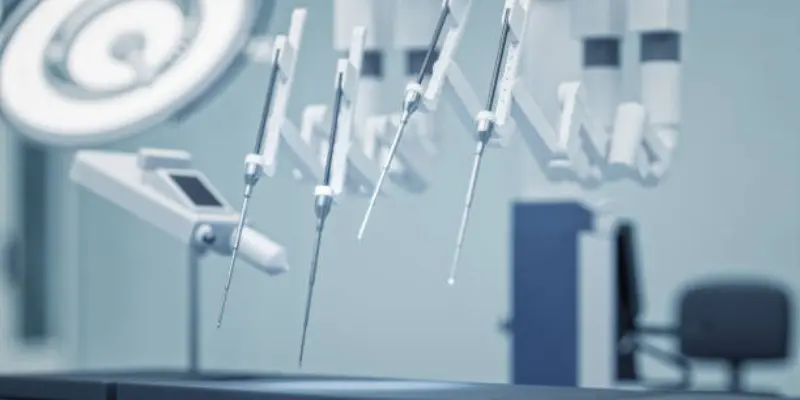

What are AI robots in surgery
AI robots in surgery are smart machines that help doctors during operations. They use artificial intelligence to follow instructions, guide tools and perform tiny movements with high accuracy. These robots don’t think on their own but act based on data and the surgeon’s control. Their main job is to make surgeries safer and more precise.
These robots are actually;
- Machines used to assist doctors during surgery
- Controlled by surgeons but guided by artificial intelligence
- Designed to perform very small and accurate movements
- Helpful in making surgeries faster, cleaner and safer
- Not fully independent, still need human control
Why AI Robots in Surgery Matter for Medical Professionals
For surgeons and healthcare teams, AI robots in surgery offer more than just new tools. They bring a new level of precision, consistency and control to the operating room.
- Improved Accuracy: These robots can follow exact paths with minimal tremors. That results in cleaner cuts, smaller incisions and better outcomes, especially in delicate procedures like heart or brain surgery.
- Reduced Fatigue: Long operations can wear out even the best surgeons. AI-assisted robots help by taking over repetitive or physically straining tasks, reducing human error caused by exhaustion.
- Better Training and Data: AI robots often record data during surgery. Professionals can review this information to learn, improve techniques and even train new staff using real case studies.
- Faster Recovery for Patients: Smaller incisions and precise work lead to fewer complications. That means shorter hospital stays and happier patients which is something every doctor and patient wants.
- Consistency Across Procedures: Robots don’t get tired or distracted. They help in standardizing the techniques, which is especially helpful in large hospitals where many teams operate on a shared workflow.
Also Read: AI Software for Dental Activities
For professionals, AI robots in surgery aren’t replacing skill but they are upgrading it.
How AI Robots in Surgery Work
AI robots don’t act alone during surgeries. They are smart tools that assist surgeons and not replace them.

Here’s how they work:
- Surgeon-Controlled: The surgeon sits at a console and controls the robot’s arms using hand and foot movements.
- AI Guidance: AI helps the robot to follow pre-planned surgical paths and adjust for small changes in real time.
- High-Precision Tools: The robot uses tiny instruments that can bend and rotate in ways human hands can’t.
- Real-Time Feedback: AI systems use cameras, sensors and patient data to guide the robot and keep movements safe and steady.
In simple terms, the robot acts as an extension of the surgeon which is more stable, more precise and more focused.
Common Misconceptions And the Truth
Let’s clear up a few myths about AI robots in surgery:
- Myth 1: Robots perform surgery on their own.
Truth: Robots never act alone. A trained surgeon is always in control. - Myth 2: AI replaces the need for human doctors.
Truth: AI supports doctors. It helps them perform better but never replace humans. - Myth 3: AI robots make surgeries riskier.
Truth: When used properly, they reduce risks by making smaller incisions and reducing human error. - Myth 4: Only big hospitals can afford them.
Truth: More hospitals, even mid-sized ones, are now adopting robotic surgery as costs slowly drop.
What Could Go Wrong And How to Fix It
Even with smart robots, things can go wrong during surgery. That’s why it’s important to understand the risks and how to deal with them.
1. Technical Errors
- What happens: The robot may freeze, lose connection or show wrong data.
- How to fix it: Always have a backup plan. The surgical team should be trained to switch to manual tools if needed.
2. Software Bugs or AI Misjudgment
- What happens: The AI might give wrong suggestions if it misreads patient data.
- How to fix it: Double-check AI inputs with human judgment. Surgeons should never rely only on AI to make decisions.
3. Learning Curve for Staff
- What happens: If doctors or nurses are new to robotic systems, they may struggle at first.
- How to fix it: Hospitals must provide proper training and allow time to practice with the system before real surgeries.
4. Mechanical Failures
- What happens: A robot arm may move slower than expected or stop working.
- How to fix it: Regular maintenance and testing before surgery prevent surprises in the operating room.
5. High Costs and Downtime
- What happens: If the system breaks, it can delay surgeries and cost a lot to repair.
- How to fix it: Use support from the robot’s manufacturer and invest in service plans to reduce downtime.
Even though AI robots in surgery bring many benefits, they still need human oversight, good training and regular care. Being prepared is the key to safe and successful use.
Types of AI Robots in Surgery And Who Can Use
AI surgical robots come in different types. Each one helps with specific tasks in the operating room. Let’s break them down.

1. Robotic-Assisted Surgery Systems
These robots are controlled by surgeons. They help with delicate movements like stitching or cutting in tight spaces.
- Best for:
Experienced surgeons who want more control and precision during complex surgeries like prostate or heart operations.
2. AI-Powered Navigation Robots
These robots guide tools inside the body using 3D maps and patient scans. They enable precise movements and prevent unnecessary cuts which shorten the recovery time.
- Best for:
Neurosurgeons and orthopedic specialists who need accurate guidance for brain or spine surgeries.
3. Autonomous Assistance Robots (Limited Autonomy)
These can do simple, repetitive tasks like holding instruments or cleaning up without direct control. They reduce the administrative burden from the surgery staff.
- Best for:
Busy surgical teams that need help with basic support tasks to save time and reduce manual effort.
4. Microrobots
These are tiny robots that go inside the body for tasks like clearing blockages or delivering drugs. These are the best type of robots which bring high accuracy during delicate surgeries.
- Best for:
Researchers and labs working on experimental treatments or minimally invasive procedures.
5. Tele-surgery Robots
These allow surgeons to operate from a distance using high-speed internet and robotic arms. These robots are vanishing the boundary hurdles that most of the patients face in healthcare.
- Best for:
Remote healthcare centers or military settings where expert surgeons are not physically available.
Each type of AI robot in surgery plays a special role. Choosing the right one depends on the surgeon’s skill, the hospital’s needs and the type of surgery being done.
Applications of AI Robots in Surgery
AI robots in surgery are changing how doctors operate. They make surgeries safer, faster and more accurate. These robots work alongside surgeons and improve results in many ways.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery
Helps in making smaller cuts and leads to quicker healing and less pain. - Precision Suturing
Assists in stitching with high accuracy, especially in tight or delicate areas. - Tissue and Tumor Detection
Uses AI to spot abnormal tissues during surgery for better decision-making. - Orthopedic Surgery Assistance
Guides bone cutting and joint replacements with 3D accuracy. - Spine Surgery Navigation
Helps to place the screws and tools in exact spots without damaging nerves. - Cardiac Surgery Support
Allows surgeons to work on the heart with tiny tools and steady movement. - Neurosurgery Planning and Guidance
Uses AI maps to guide instruments through the brain safely. - Data Collection for Post-Surgery Review
Records surgical steps for learning, reviews and performance improvement. - Remote Surgery (Tele-surgery)
Lets expert surgeons operate from another location using computerized robots. - Surgical Training and Simulation
Trains new doctors with robot-guided simulations that feel like real surgery.
Pros and Cons of AI Robots in Surgery vs. Traditional Surgery
If we compare the dark and bright sides of both traditional and AI-assisted robotic surgeries, we can conclude the real game changing capabilities of AI robots in surgeries. I am going to discuss the advantages and disadvantages of AI robotics surgeries and then will do the same for traditional surgeries.

Pros of AI Robots in Surgery:
- AI robots can make highly precise movements that reduce human error which is especially helpful in delicate surgeries like brain or heart surgery.
- Robots can perform surgeries with smaller incisions, leading to less pain, quicker recovery and fewer complications compared to traditional open surgeries.
- AI robots help surgeons by reducing physical strain which allow them to perform longer surgeries with less risk of error due to fatigue.
- AI robots can provide real-time data and 3D imaging during surgeries, which enhances decision-making and increases the safety of complex procedures.
- AI robots follow pre-programmed plans and make consistent results possible with minimal variation across procedures.
Cons of AI Robots in Surgery:
- Robotic systems are expensive to purchase and maintain, making them inaccessible for some hospitals and healthcare facilities.
- Like any technology, AI robots can experience malfunctions or connectivity issues which could delay surgeries or require a switch to manual tools.
- Surgeons need time to train and adapt to robotic systems. This transition can be challenging and may slow down initial surgery times.
- In unpredictable situations, AI robots may struggle to adapt as quickly as experienced surgeons can.
Pros of Traditional Surgery:
- Traditional surgery relies on standard tools that are generally cheaper and easier to maintain than robotic systems.
- Surgeons can make quick decisions and adapt to changes during surgery, using their judgment and skill to navigate complex situations.
- Traditional surgery is available in almost all hospitals with no special equipment or training needed.
Cons of Traditional Surgery:
- Manual procedures depend on the surgeon’s skill and focus which can lead to more mistakes compared to robotic systems with AI precision.
- Traditional surgeries often require larger incisions which result in longer healing times and more discomfort for patients.
- Surgeons can get tired after long operations which can affect the outcomes, especially in complex procedures.
Conclusion:
AI robots in surgery offer advanced precision, safety and support but they come with high costs and a learning curve. On the other hand, traditional surgery is cost effective, flexible and widely accessible but it can involve higher risks of human error and longer recovery times.
As AI technology continues to evolve, the potential of AI robots in surgery is bound to grow, bringing even greater improvements in patient outcomes and surgical efficiency. By exploring and embracing these innovations, healthcare professionals can be at the forefront of transforming the future of surgery. The future of medicine is exciting, don’t miss out on the opportunity to be part of this revolutionary change!
Related Queries
Here are frequently asked questions about AI robots in surgery;
When used properly by trained professionals, AI-assisted surgeries are generally considered safe and often result in fewer complications. Studies show patients typically experience less pain, smaller scars and faster recovery times. However, as with any surgery, there are always some risks involved.
Robotic surgery typically costs more than traditional surgery due to the expensive equipment and specialized training required. The initial investment for hospitals can range from $1-2 million per robotic system plus maintenance costs. However, these costs are gradually decreasing as the technology becomes more widespread.
Most insurance companies cover robotic surgery if it’s deemed medically necessary, similar to traditional surgical procedures. Coverage depends on your specific insurance plan and the type of surgery being performed. It’s always best to check with your insurance provider before scheduling any procedure.
AI robots are frequently used in urological procedures like prostate surgery, gynecological operations, cardiac surgery and general surgical procedures. They are particularly valuable for surgeries requiring precise movements in confined spaces. Orthopedic and neurological surgeries also increasingly benefit from robotic assistance.
Yes, recovery is typically faster because robotic surgery usually involves smaller incisions and less tissue damage. Patients often experience less pain and bleeding, leading to shorter hospital stays. Many patients return to normal activities within days rather than weeks.
Robotic systems are not ideal for emergency surgeries where speed is critical or when rapid adjustments might be needed. Some extremely complex procedures or those requiring special tactile feedback might still be better performed traditionally. The decision ultimately depends on the surgeon’s expertise and the specific circumstances of each case.
The learning curve typically ranges from 20 to 80 cases, depending on the complexity of procedures and the surgeon’s previous experience. Most surgeons require several months of training and supervised practice before becoming proficient. Hospitals usually implement structured training programs to ensure competency.
No, AI surgical robots are not available in all hospitals due to their high cost and specialized training requirements. They are more common in large urban medical centers and teaching hospitals. However, as costs decrease and benefits become more widely recognized, more mid-sized hospitals are adopting this technology.
While AI robots enhance precision, they can experience technical issues or malfunctions like any technology. The robot follows the surgeon’s commands and AI guidance, so human error in programming or control remains possible. This is why surgical teams always have backup plans and can switch to traditional methods if needed.
To learn more, you can look into professional medical journals, online resources, and technology blogs. Attending medical technology conferences or watching surgical demonstrations can also provide deeper insights. As AI technology advances, there will be plenty of opportunities to stay informed and up-to-date.